Response to Climate Change
Governance

- Board of Directors
-
- Review progress and performance every quarter
- Sustainability management system, mid- to long-term business plan, budget, etc.
- ESG Committee
-
- Hold semi-annual meetings
- Oversee the company's strategy, policies, and performance related to ESG, including climate change
- ESG Steering Committee
- Production
- Marketing
- Finance
- Planning
- HR
- Legal
S-OIL has set green advancement in response to climate change as one of its strategic goals, and the Board of Directors, the highest decision-making body, reviews the progress and performance on a quarterly basis. Detailed implementation tasks for climate action are reflected in the Company's sustainable management system, mid- to long-term business plans, and budgets, and are set by the Board of Directors. The Company regularly reviews and analyzes the gap between climate-related targets and actual performance and develops concrete measures to achieve targets. In addition, S-OIL held three executive workshops in 2020 to respond to climate change and enhance its sustainable management system, and in 2021 the Company established an ESG Steering Committee composed of executives from each function, including production, marketing, finance, planning, human resources, and legal, to review, evaluate, and make decisions on ESG KPIs and other key issues at regular quarterly meetings. In 2022, the Company established the ESG Committee under the Board of Directors, which was formally approved at the 2023 Annual General Meeting. The ESG Committee oversights the Company's overall strategy, policies, and performance on ESG issues, including climate change, and meets regularly semi-annually.
Strategy
S-OIL considers various scenarios related to climate change when developing its mid- to long-term strategy and gives primary consideration to the scenario of Korea's Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), which aim to limit the global temperature increase to well below 2℃ above pre-industrial levels. Based on this, the Company forecasts mid- and long-term emissions and reduction requirements and implements a comprehensive emissions management plan with cost-effective countermeasures. Furthermore, S-OIL has established a decarbonization roadmap to achieve carbon reduction by 35% compared to 2030 BAU and is promoting low-carbon investments that consider both technology readiness level and economic viability, while developing business models that can serve as new engines of growth. The Company also operates an Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) system that systematically and regularly analyzes a wide range of potential risks in a rapidly evolving business environment and uses it to identify the risks and opportunities associated with climate change.
Climate-related Risks and Opportunities
Climate-related Risks and Opportunities : Climate-related risks and opportunities, Timeframe, Financial impacts, Responses
Climate-related risks
and opportunities |
Timeframe* |
Financial impacts |
Responses |
Transition Risks
- policies and regulations |
Emission
trading
scheme |
Short-term/
Mid-term |
- (Negative)
- Government allocation of emission allowances expected to decrease → Increased burden of GHG reductions and costs due to higher emission allowance prices
- (Positive)
- Sale of surplus emission allowances by further reducing direct GHG emissions
|
- Introduce energy efficiency facilities such as waste heat recovery units and combined-cycle gas turbine generator
- Develop a roadmap for securing credits based on Korea's NDCs and the company's decarbonization roadmap
|
Mid-term/
Long-term |
- (Negative)
- Increase in global regulatory compliance costs including EU CBAM and US CCA
|
- Establish carbon emissions calculation system for each product
|
Stricter
climate
disclosure
regulations |
Short-term/
Mid-term |
- (Negative)
- Decreased corporate value and increased litigation costs in the event of legal action for failure to disclose climate information, poor low-carbon performance, etc.
|
- Comply with climate disclosure standards under the EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
- Share guidelines and policies to prevent greenwashing across the organization
|
Transition Risks
- markets |
Declining demand
for fuel/lube
products and
growing demand
for low-carbon
products |
Short-term |
- (Positive)
- Increased sales of circular economy products
|
- Produce products using bio-based fuel and waste plastic pyrolysis oil
- Obtain globally recognized ISCC certification for our product lines
|
Mid-term/
Long-term |
- (Negative)
- Decrease in demand and sales due to global regulations such as the ban on sales of ICE vehicles and the international aviation carbon offset scheme
- (Positive)
- Reduced cost of adoption and investment in CCUS technologies, biofuels, and recycling technologies
|
- Identify new CCUS business opportunities in existing processes
- Expand and develop new energy businesses such as hydrogen business, renewable fuel, etc.
|
| Physical Risk |
Heat waves |
Short-term/
Long-term |
- (Acute/Chronic)
- Delays in periodic maintenance and higher chiller costs
- All SSP scenarios1) are projected to exceed 20℃ as early as 2026.
- Heat wave days are also predicted to exceed 30 days in the 2060s under SSP 5-8.5 scenarios, reaching up to 96.4 days in 2100
|
- Provide facilities to prevent health hazards and slowdowns for outdoor workers during summer months
|
| Precipitation |
Short-term |
- (Acute)
- Increased operating costs due to river flooding and disruptions to plant operations due to increased precipitation intensity and peak precipitation amounts
SSP 5-8.5 scenario predicts over 350 mm of precipitation in 2026
|
- Update risk response manual for stronger typhoons and heavy rains
- Conduct maintenance of wastewater discharge facilities
|
Short-term risk : 1-2 years / Mid-term risk : 3-5 years / Long-term risk : 6-10 years
GHG Management through Advanced Carbon Management System
S-OIL operates an IT-based carbon inventory system to identify, record, calculate and report GHG emissions generated by its business activities for systematic GHG management. The system reflects changes in government regulations in real time and ensures data accuracy and reliability through internal verification and independent external assessment. Through regular maintenance of measurement and analysis equipment, the Company maintains the highest standards in the industry with advanced monitoring capabilities. The Energy Conservation & Operation System (ECOS) evaluates the company's energy use and identifies areas for improvement, which are then incorporated into processes to save energy and reduce GHG emissions.
The Company also has revised its internal procedures through top management meetings to improve the efficiency of carbon management and to integrate climate change into investment decisions by considering GHG costs not only for major new investments, but also for small and medium-scale process improvements. In addition, to enable cost-effective regulatory responses, a medium- to long-term emissions trading scheme has been established, projecting future emissions and available credits based on the national GHG reduction roadmap.
Minimizing Direct and Indirect Emissions
Improving Energy Efficiency and Installing Low-Carbon Utilities
To minimize direct and indirect carbon emissions from our operations, the Company is continuously investing in the use of energy-efficient heat exchangers, waste heat recovery, process efficiency improvements, and offsite low-carbon steam. The Company is also working to implement gas turbine cogeneration using clean gas fuel.
Expanding Carbon Capture, Utilization and Storage (CCUS) Business
The Company has been producing carbonated products such as liquid carbon dioxide and dry ice for beverages by capturing and utilizing approximately 100,000 tons of carbon dioxide from hydrogen production in cooperation with a neighboring company. In addition, the Company generated a profit of KRW 280 million in the four months of 2023 by completing construction early and doubling the amount captured.
Carbon Emission Reduction Projects at Home and Abroad
S-OIL joins global efforts to respond to climate change by participating in overseas carbon credit projects. In 2019, the Company decided to invest in a project to distribute free high-efficiency cookstoves in Myanmar. The stoves are more energy efficient than burning wood for fuel, reducing carbon dioxide emissions and, most importantly, improving the quality of life for Myanmar's people, who are affected by drought, flooding, typhoons, and severe air pollution that kill scores of people every year.
Also in 2020, the Company participated in a project to build community drinking water facilities to provide safe drinking water to villagers who did not have access to public water supplies and had to boil their water by burning wood. Since 2021, the Company has built a total of 20 drinking water facilities, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by reducing the amount of wood that would otherwise be used to purify water, improving the human rights of women and children who would typically provide the labor to collect and purify water, and contributing to improved health conditions such as the prevention of water-borne diseases.
The Company plans to participate in various carbon emission trading initiatives both domestically and abroad to secure additional carbon credits under an evolving carbon trading scheme. At the same time, the Company will continue to diversify into low-carbon, eco-friendly businesses as a way to reduce the carbon intensity of our overall sales and mitigate climate change risks.
Carbon Reduction Initiatives with Stakeholders
-
- Encourage active participation in energy and greenhouse gas reduction by turning best ideas into projects and expanding incentives.
- (2023) Award CO2 capture expansion project with neighboring company
- (2023) Contribute to the company's profitability and carbon emission reduction with stable sales of approximately 300 tons of CO2 per day

-
- Raise awareness of GHG emissions reduction through various activities
- (2023) Introduce e-receipt on mobile application as first refiner to do so
-
- Make annual decisions about activities and memberships based on their potential to make a lasting positive impact on the environment
- Reconsider joining an association that does not comply with the Paris Agreement or engages in activities that may harm the environment, and work to mitigate the effects of climate change
Risk Management
Integrating Climate Risks into ERM
S-OIL has integrated climate change risk identification and assessment processes into the ERM system for systematic management. In 2020, the Company raised the importance of climate change risk in line with accelerated efforts to achieve carbon neutrality and strengthened the process of identifying, assessing, monitoring, and responding to risks.
The Sustainability Management Team, as the risk owner for climate change, performs a quarterly quantitative assessment of climate-related issues and establishes a risk response process. In addition, the ERM Committee, composed of senior executives including the CEO, conducts a final review of risk management activities, including climate change, on a quarterly basis, determines necessary responses, and makes decisions on company-wide risk management policies.

-
- Perform environmental change analysis in the categories of political, economic, market, technology, social, and legal

-
- Evalute the relative importance of risks based on the Risk Assessment Matrix, which is built around the probability and impact of each risk
- Sustainability Management Team (risk owner) : Conduct quantitative assessment of climate-related issues every quarter
-
- Establishment of a process within ERM to ensure the rapid and effective implementation of risk mitigation controls on a company-wide basis in the event of a risk with a material impact on the company
- ERM Committee : Conduct a final review of risk management activities including climate change every quarter, plan necessary responses and make decisions on risk management policies
Disaster Response Activities
S-OIL is well aware of the physical risks posed by climate change. In particular, the Onsan Refinery is exposed to high physical risks due to high riverine flooding stress2), as shown by our risk monitoring using the World Resource Institute's (WRI) Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas1). In response, the Company has implemented a proactive disaster response system. In response, the Company have implemented a proactive disaster response system. By monitoring data from the Korea Meteorological Administration and responding in a timely manner, the system is designed to minimize the impact of natural disasters such as typhoons, storms, heavy rains, earthquakes, and tsunamis, which can cause disruptions in production and crude oil supply, as well as environmental pollution.
Metrics & Targets
The reduction of greenhouse gas emissions has been identified as one of the key performance metrics for the achievement of our strategic objectives, and to reduce emissions, facility investments and emissions status are regularly monitored and the results are incorporated into the performance evaluation of all executives and team leaders. Short-term initiatives to reduce carbon emissions are reflected in company-wide KPIs to closely manage their implementation and progress, while medium- and long-term plans to reduce carbon emissions are updated on an annual basis in the ESG Roadmap in light of changes in global carbon emission policies. Based on the mid- to long-term operating plan and the NDC scenario, the Company has set a quantitative target of '35% reduction in carbon emissions from BAU in 2030'. To this end, the Company has established a specific roadmap for achieving the target and are implementing it in stages by prioritizing actions based on feasibility and economic viability, including technological maturity. The Company has also developed KPI indicators using carbon intensity and carbon abatement, and monitor the implementation of carbon reduction measures on a monthly basis.
Reduction in greenhouse gases : Category, 2023 Targets, Performance in 2023, 2024 Targets, Mid/Long-term Targets
| Category |
2023 Targets |
Performance in 2023 |
2024 Targets |
Mid/Long-term Targets |
| Strategic carbon response |
Expansion of direct GHG
emissions reduction |
Implemented
35 carbon reduction
initiatives (-249ktCO2eq) |
Expansion of direct GHG
emissions reduction
Development of low-carbon, eco-friendly businesses |
- |
| Overseas CDM project development |
Participated in CDM projects
in Myanmar and Bangladesh |
Domestic/over-seas
CDM project development |
- |
Carbon Intensity
(t/kCWB) |
6.27 |
6.27 |
6.26 |
- |
Carbon Abatement
(ktCO2eq) |
-190 |
-249 |
-60 |
35% reduction from 2030 BAU |
Operational Efficiency Improvement
Governance
S-OIL's Downstream Transformation Program, launched in 2022, is an ongoing, enterprise-wide effort to improve operational efficiency and profitability across all business areas. Each function voluntarily identifies and implements initiatives and then measures their performance. The Project Management Office aggregates the performance of each initiative and manages it as an enterprise KPI, while the Value Validation Office validates performance. The performance and progress of the Downstream Transformation Program is regularly reported to top management and the Board of Directors by the Corporate Planning Division, the Chief Transformation Office. This systematic process ensures that the program is not a one-time event, but rather a continuous effort to optimize operational efficiency and profitability.
Downstream Transformation Governance
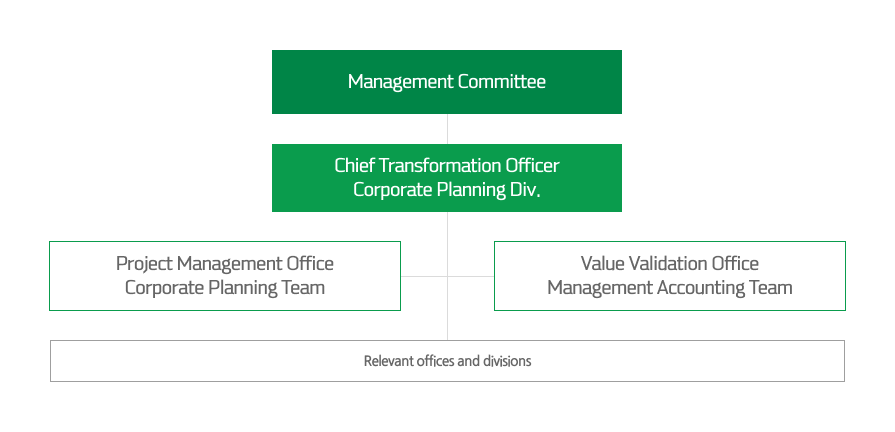 Management Committee - Chief Transformation Officer Corporate Planning Div. - project management office Corporate Planning Team / Value Validation Office Management Accounting Team - Relevant offices and divisions
Management Committee - Chief Transformation Officer Corporate Planning Div. - project management office Corporate Planning Team / Value Validation Office Management Accounting Team - Relevant offices and divisions
As for the Refinery, the Refinery Minor Investment Analysis and Screening Committee is held on a regular basis, and various investment activities are evaluated for their potential contribution towards efficient operations and improved profitability. In addition, the S-OIL Integrated Manufacturing Operations Management System (S-IMOMS) project is underway to improve safety and work efficiency by moving towards a digital refinery that will integrate the major systems within the refinery.
Strategy
Downstream Transformation Program
In the face of rapidly changing market conditions and external factors beyond our control, it is critical to identify and execute revenue-generating opportunities to drive sustainable growth. The Downstream Transformation program has been launched to identify and drive additional value creation opportunities across the organization to improve the competitiveness of existing operations.
The program, developed through studies with leading consulting firms, has enabled us to identify, roadmap, and implement cost-effective initiatives. While implementing the initiatives, the Company also tracks their contribution to profitability, both in terms of improving margins and reducing costs. In 2023, the Company integrated the Downstream Transformation program with the Unplanned Profitability Improvement program to execute profitability improvement activities more systemically.
Profit Improvement Suggestion System and Communication Activation
In order to strengthen our efficiency and competitiveness, the Company continues to implement systematic profit improvement measures throughout the entire process, from crude oil procurement to product manufacturing and shipment. To this end, the Company uses various channels, including the company-wide employee suggestion system, to solicit and implement creative ideas for improving profits, which may include improving facilities, introducing new technologies, optimizing operating conditions at production facilities, increasing production capacity for high-value-added products, reducing fuel consumption, adjusting product mix ratios, etc. The Company has created an environment in which employees are free to propose new ideas at any time through the dedicated Profit Improvement Suggestion System. The Company also operates a separate suggestion system called Suggestion Well, which allows employees to freely submit ideas to encourage innovation across the company.
To motivate profit improvement activities, the Company incentivizes employees who are actively involved in profit improvement, and since 2017, the Company has selected and recognized 16 teams in each of the first and second halves of the year. The Company also has the S-OIL Refinery Improvement Communication Hub (S-RICH) system for sharing and reference of best practices in profit improvement, which also contributes to the implementation of the Decision Support & Visualization (DSV) system as part of a digital transformation drive.
Activities for Improving Energy Efficiency
S-OIL has made operational efficiency one of its strategic goals, and is practicing energy management with the aim of achieving the first quartile of the Solomon Fuel Energy Intensity Index (EII)* in the Asia-Pacific region. To this end, the Company strives to continuously reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency. The Company does this through external energy consulting as well as through in-house energy saving initiatives developed by our engineers.
Solomon Fuel Energy Intensity Index (EII) : An energy efficiency indicator for refineries, compared to standard refineries of similar size and configuration.
-
- Energy performance monitoring through real-time energy dashboard (ECOS)
- Energy performance gap analysis through regular review
- Daily EII Report, Weekly EII status review, Monthly KPI review
- Quarterly performance review by energy session
- Yearly Company wide EII Review, etc.

-
- In-house development of energy saving ideas through refinery-wide collaboration
- Energy saving study in consultation with external experts
- New energy saving initiatives
- Introduction of External Energy Source
Gas Turbine Generator (GTG) Installation
S-OIL has been preparing to invest in new self-generating facilities that will run on clean natural gas to generate clean electricity and produce steam by recovering waste heat. The Company completed the feasibility study in 2022 and basic design in 2023. The self-generation facilities are expected to be more efficient than the electricity supplied by KEPCO, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and improving air quality. By using all the electricity generated by the GTGs, the Company can also contribute to the stability of the national power supply.
External Electricity Energy Saving Consulting
The Company has signed a contract with a specialized energy consulting company to provide power saving services at our Refinery from the second half of 2023 as a way to proactively respond to changes in the energy environment, such as the rising unit cost of electricity. The Company aims to improve energy efficiency and reduce energy costs at our Refinery by implementing various ideas for saving electricity.
Education to Raise Awareness of Energy Consumption Reduction
S-OIL conducts activities aimed at raising awareness among employees to promote cultural change for energy optimization and consumption reduction. Key activities include distributing posters on energy savings throughout the energy plant, introducing energy-saving technologies through dedicated sessions, and awarding teams with significant energy-saving practices and those with numerous energy-saving proposals at the end of the year. Through these efforts, the Company aims to enhance employees' awareness of energy conservation.
- Energy Commitment Statement
- View PDF
Digital Transformation (DT) Roadmap Implementation
S-OIL promotes digital transformation innovation tasks that leverage the core technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. A three-year digital transformation roadmap was established in 2020, and projects were implemented through 2023. Subsequently, the Company established a new roadmap from 2024 to 2026 and selected digital transformation tasks relevant and impactful to our organization by researching latest technology trends and best practices, with the goal of further increasing work productivity and reducing costs.
In the process of developing the roadmap, the Company analyzed existing digital transformation directions and status quo, and identified various digital projects that could be applied to the industry. This led us to define and prioritize 19 digital transformation projects based on their strategic importance and ease of execution. On the basis of these assessments, a three-year implementation plan for the projects has been drawn up, and the Company will continue to monitor their progress.
Launch of Digital Refinery Project and Adoption of 4IRT
Since 2018, the Company has been working on the 4IRT (4th Industrial Revolution Technology) initiative as a strategy for the acceleration of the Digital Refinery. Through technology research, the Company has identified 38 items that are applicable to the company and are rolling them out sequentially in the Refinery. At the same time, the Company is constantly on the lookout for new technologies for the Digital Refinery by understanding the trends in the market and by responding to technological advances in the industrial field through exchanges with other companies. The Company has already adopted 4IRT technologies, including drone inspection, smart helmets and intelligent CCTV, to build a safe and efficient digital refinery. And in 2023, seven technologies, including facial recognition, worker positioning device, and robotic process automation (RPA), have been rolled out with a focus on preventing accidents and casualties while improving work efficiency. Other technologies, such as ultrasonic cameras and digital locks, are being applied on site, and various other technologies, such as four-legged robots, AI vision, and forklift safety control systems, are being studied in depth.
Risk Management
S-OIL recognizes lagging behind in digital transformation as a major risk to the company, where business value is not created and corporate competitiveness is weakened due to failure to timely implement digital transformation using Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies. To address this risk, the Big Data team in the IT Division, which is the risk owner, performs risk management activities, including assessing the risks, and reports the results to the risk owner. The risk owner, the Head of IT Division, then presents the results of the risk assessment to the ERM Committee, which consists of top executives, including the CEO. The ERM Committee carries out regular risk response activities on a quarterly basis and takes the necessary decisions in the event of a crisis.
In particular, if a digital transformation project is delayed for more than three months due to adverse conditions in the internal and external business environment, the ERM committee is informed, and the Digital Transformation PM team reviews the project progress and reports the results to Risk Management. Risk management prepares a plan for change to the digital transformation master plan and reports it to the risk owner, who then presents it to the ERM committee for approval. Once approved, the revised plan is implemented in coordination with the Digital Transformation PM team.
Metrics & Targets
Downstream Transformation and Profit Improvement Activities Metrics and Targets
The business environment in 2023 has been more challenging than ever due to the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war and escalating geopolitical crises in the Middle East, leading to energy price volatility for crude oil and natural gas and a global economic downturn. Despite these challenging conditions, S-OIL achieved significant results in 2023 by increasing the production of high-value-added products, improving product yields, saving energy, and optimizing product shipments.
Since 2013, the Company has consistently engaged in activities to identify and manage profit improvement items, making it increasingly difficult to discover new items. However, through the Downstream Transformation program, the Company plans to continue and intensify its profit improvement activities to enhance the Company's competitiveness.
Downstream Transformation and Profit Improvement Activities Metrics and Targets : Category, 2023 Targets, Performance in 2023, 2024 Targets, Mid/Long-term Targets
| Category |
2023 Targets |
Performance in 2023 |
2024 Targets |
Mid/Long-term Targets |
| Reinvigorating Employee Suggestion Program |
Revitalizing the program |
218 participants,
888 proposals submitted |
Revitalizing the program |
Revitalizing the program |
Energy Efficiency Improvement Metrics and Targets
S-OIL strives for continuous energy savings and efficiency improvements through energy consulting from external experts and our own energy-saving ideas discovered by in-house engineers. Additionally, S-OIL analyzes the before-and-after performance of energy-saving measures and prepares internal reports to document the improvement effects. The Company also compiles and manages monthly results for energy-saving items to continuously verify the effectiveness of its energy conservation efforts. In 2023, the Company achieved the target for the year by discovering energy saving ideas equivalent to an annual EII improvement of 0.68. In 2024, S-OIL will continue to explore new energy improvement opportunities through its internal activities and external consulting, with a focus on reducing production variable costs and reducing carbon emissions.
Energy Efficiency Improvement Metrics and Targets : Category, 2023 Targets, Performance in 2023, 2024 Targets, Mid/Long-term Targets
| Category |
2023 Targets |
Performance in 2023 |
2024 Targets |
Mid/Long-term Targets |
| Identifying ideas for EII improvement |
Idea discovery equivalent to annual EII improvement of 0.3 |
Discovered ideas equivalent to annual EII improvement of 0.68 |
Idea discovery equivalent to annual EII improvement of 0.2 |
Achieving EII 1st quartile in Asia-Pacific region |
Digital Transformation Metrics and Targets
The key to successful digital transformation is to implement projects without delay and according to the established roadmap. That is why the Company has set 'DT project implementation' as a corporate KPI and report progress and plans to the company's top management on a monthly basis. This allows us to systematically monitor the progress of digital transformation projects in the pipeline and ensure transparency on achieving key objectives across the organization.
Specifically, the Company manages the progress of digital transformation projects against plan as a corporate KPI, and in 2023, all four planned projects were delivered with 100% adherence to timelines. For 2024, the Company has 10 digital transformation projects in the pipeline, and the Company is on track to implement them on time.
Digital Refinery
Through the DT project, in which the Company benchmarks Saudi Aramco for the implementation of S-imoms, an integrated digital platform, the Company aims to transform business processes by leveraging the latest digital technologies to improve safety, reliability and efficiency in refinery operations, reliability & integrity and compliance.
S-OIL's goal is to successfully complete the first phase of S-imoms by launching a total of 13 solutions by early 2024, driving innovation in the Digital Refinery. By setting quantitative indicators as KPIs, the Digital Transformation team tracks the progress of the S-imoms project.
Digital Refinery : Category, 2023 Targets, Performance in 2023, 2024 Targets, Mid/Long-term Targets
| Category |
2023 Targets |
Performance in 2023 |
2024 Targets |
Mid/Long-term Targets |
S-imoms Project
progress score (%) |
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
Pollutant Management
Governance
Environmental Management System
S-OIL has set the establishment of 'Proactive Green Management' as the company's top environmental policy. To this end, the Company produces high-quality, environmentally friendly products by continuously improving processes and environmental facilities and introducing new technologies, while also striving to acquire pollution abatement facilities such as desulfurization and denitrification units, advanced wastewater treatment facilities, and dust collection facilities. Since 1996, the Company has practiced the highest level of environmental management by obtaining the first ISO 14001 environmental management system certification for all production processes and completing the 9th renewal in 2023, and has expanded the scope of certification to terminals to apply and manage the environmental management system throughout the process until the final product is shipped. In 2023, environmental training was provided to 1,100 employees to acquaint them with environmental laws and regulations and the company's environmental management policies and systems.
- ISO 14001 Certification
- View PDF
Environmental Policy
S-OIL has established and operates an advanced environmental management system under the principle of preventive green management that prevents environmental hazards and risk factors at every stage of business operation. In addition, the Company complies with the following environmental policies with the cooperation of stakeholders such as customers, suppliers and employees.
- The Company shall comply with the environmental laws and regulations of the region in which the Company operates its business, establish strict internal standards that are above legal standards, and adhere to the standards.
- The Company shall minimize the environmental pollutants (air pollutants, water pollutants, soil pollutants, hazardous chemicals, etc.) created in the production processes or business facilities through the improvement of efficiency, etc. and prevent potential environmental accidents including oil spill.
- The Company shall develop, manufacture and sell highly efficient products that minimize environmental impact on consumers.
- The Company shall minimize greenhouse gas emissions from the distribution process through efficient logistics system operation and prevent environmental accidents such as leakage.
- The Company shall treat wastes safely and environmentally, and improve waste reuse.
- The Company shall consider environmental factors when selecting suppliers and do not receive products and services from suppliers that can cause severe environmental pollution while expanding green purchasing.
- The Company shall improve the environmental performance of affiliated companies such as JVs and subsidiaries, and also consider environmental factors in capital investments such as mergers and acquisitions.
- The Company shall actively support and participate in environmental protection activities such as biodiversity conservation.
Strategy
Environmental Pollutant Emissions Management
S-OIL has been operating the Environmental Management Dashboard System since 2021 to proactively respond to the strengthening of environmental laws and regulations. The system visualizes various environmental indicators, such as pollutant emission concentration, emission volume, and wastes disposal status, and provides real-time data, thus improving the accessibility of environmental data for users. The Company also proactively responds to environmental regulations by updating the system in real time with major legal and regulatory revisions and regular statutory audit schedules.
Air Quality Management
S-OIL has more stringent internal emission standards than the legal requirements in order to improve the air quality in local communities.
Key activities related to air quality
Key activities related to air quality : Key activity, Description
| Key activity |
Description |
| Minimizing SOx / NOx / dust emissions |
- Replaced all heater and boiler fuel since 2018 (Bunker-C → gas fuel)
- Operating the wet scrubber / dry scrubber (electric/filtering)
- Installing Ultra Low NOx Burner (ULNB), Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR), etc.
|
| Reducing and better managing volatile organic compounds |
- Installing Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer (RTO), Vapor Combustion Unit (VCU)
- Installing leak prevention facilities (sealing devices, leakage prevention materials, etc.) in internal floating roof storage
- Operating Leak Detection and Repair (LDAR) system for fugitive emissions* of hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) throughout the entire process, including storage, shipping, etc.
- 2023 Performance: Achieved a leak rate of 0.03% against the Company's own leak baseline of 500 ppm
|
| Voluntary agreement to reduce air pollutants |
- Targeted 40% reduction from 2014 level by 2022. Final results exceeded target by 62.3%.
- Aiming to reduce emissions by 40% compared to 2016 level by 2024. Efforts underway to achieve this goal.
|
| Other initiatives |
- Reducing pollutant emissions through environmental investments (e.g., energy efficiency improvements and facility upgrade) and efficient operation of pollution prevention facilities
- Met the emission quota granted under the Air Pollutant Emission Cap established in 2020. Planning to meet the quota in 2024 by reinforcing the management of prevention facilities
|
Fugitive Emissions : leakage of pollutants into the atmosphere from equipment, transmission pipes, seals, valves, etc., other than through a normal outlet such as chimneys or vents.
Water Quality Management
S-OIL engages in a number of environmental protection activities to minimize its impact on water quality in the waters surrounding the Refinery and to conserve water resources.
Key activities related to water quality
Key activities related to water quality : Key activity, Description
| Key activity |
Description |
| Reducing water pollutant emissions and complying with legal standards |
- Operating wastewater treatment facilities reliably to minimize impact on surrounding waters
- Removing contaminants through physical, chemical, and biological processes to treat wastewater
- Ensuring thorough preparedness for emergencies by transmitting water quality data in real-time to administrative agencies via Tele-Monitoring System (TMS)
- Expanding heavy summer rainwater storage facilities and introducing a separation system for rainwater and wastewater
- Strengthening monitoring of 32 specific substances harmful to water quality including Cu and Pb as well as general water pollutants
- Minimizing water quality impacts to public water bodies by establishing strict management standards, expanding analysis categories, and conducting internal/external analysis of cooling tower blowdown water discharged directly to the outside, beginning in 2023.
|
| Minimizing water usage growth and increasing reuse |
- Removing H2S and NH3 from sour water generated from the production process and reusing or reclaiming it in the production process
- Monitoring and managing water usage and recycled water on a regular basis
|
Soil Quality Management
In order to prevent soil contamination at the refinery and terminals, including oil storage facilities, the Company conducts regular internal inspections and accept statutory inspections. The Company also systematically improves facilities, such as the installation of pipes on the ground instead of underground. In addition, when building or rebuilding service stations, the Company applies the concept of clean, environmentally friendly service stations by using double tanks and double piping to prevent oil leaks, and leak detection and alarm systems to quickly prevent the spread of contamination in the event of a leak.
Hazardous Chemical Management
S-OIL complies with the standards for handling hazardous chemicals and associated facilities in accordance with the Chemical Substances Control Act. The Company also enhances our response capability in the event of a chemical accident through regular emergency drills. Additionally, the Company implements thorough accident prevention and response activities through the 'Chemical Accident Prevention and Management Plan' through which the Company creates accident scenarios for the hazardous chemicals the Company handles, calculate the extent of the impact, prepare a summary of chemical accident risks and emergency response information, and notify the local community once a year. In 2023, the Company thoroughly implemented the approved chemical accident prevention management plan and chemical substance permit, and strengthened our chemical accident prevention and response capabilities through external inspections.
Wastes Management
S-OIL strives to consistently reduce wastes disposal and increase wastes recycling through strict segregation of wastes storage and treatment, thus promoting sustainable resource cycles. Fire detectors and water sprinklers have been installed in wastes and wastes catalyst storage facilities to prevent potential fire accidents and contamination during the wastes storage process.
Risk Management
Approval of Integrated Environment Permits by the Ministry of Environment and Subsequent Activities
Pursuant to the Act on the Integration of Environmental Pollution Management, S-OIL obtained the 'Integrated Environmental Permit' from the Ministry of Environment in December 2022. The Integrated Environmental Permit is a system introduced to solve the problems of environmental permits under individual laws and regulations. It consolidates about 10 environment-related permits into one integrated permit, while applying customized emission standards that take into account the impact on the surrounding area of the business site to conduct integrated and systematic environmental management.
S-OIL has improved various environmental facilities and complied with the enhanced emission permit and management standards under the Integrated Environmental Permit. To maintain compliance with laws and regulations and to minimize the generation of pollutants, the Company plans to make further improvements to our facilities.
In 2023, the Company developed an IT-based Integrated Environment Management System (IEMS) to systematically and efficiently manage items required by law to be submitted to the Ministry of Environment for follow-up activities under the Integrated Environmental Permit.
The IEMS has improved work efficiency by automatically completing approximately 1,900 process facility operating parameters that were previously completed manually, and contributes to environmental compliance by preventing risks of non-compliance such as failure to meet legal submission deadlines and incorrect or missing data.
Environmental Impact Assessment and Environmental Compliance
S-OIL has been recognized as an environmentally friendly company that faithfully complies with the Environmental Impact Assessment Act and fully considers possible environmental impacts on neighboring areas. When undertaking new projects and large-scale construction, the Company evaluates the impact on the Company's facilities and surrounding areas through an environmental impact assessment company. This assessment helps us incorporate pollution reduction measures into the design, and periodic measurements of air, water, biodiversity, and soil quality are conducted for follow-up management. The results of the environmental impact assessment are submitted to the administrative authorities before the start of the project, and follow-up environmental impact assessments are carried out during and after the project to minimize any environmental impact.
The Company proactively responds to environmental policies and regulations in accordance with our environmental policy of "Proactive Green Management". The Company considers environmental management from the initial plant construction stage by introducing optimized pollution prevention facilities and strive to minimize environmental impact by strictly observing regulations and internal standards as well. The Company further strengthens our voluntary environmental management system by proactively conducting daily checks and promptly initiating corrective actions for any deficiencies, while improving our environmental management by closely monitoring changing environmental policies and laws on a monthly basis. In addition, the Company reviews and shares revisions to environmental regulations through the Legal Compliance System and self-inspection checklists. Periodic self-assessments are conducted using the Environmental Compliance Assessment List, and implementation is verified through internal audits.
S-OIL promotes eco-friendly management by applying rigorous internal standards, while continuously communicating with various stakeholders such as the local community, government, media, and academia to collect and analyze environmental trends and actively incorporate them into our environmental management system. The Company also shares information about our environmental management with local residents and related organizations and listen to their opinions to improve our environmental management activities. To promote environmental protection and establish close ties with the local community, the Company actively participates in various environment-related events in the local community. The Company also contributes to the development of the local community by providing environmental training materials to our suppliers and consulting services to small businesses in neighboring areas.
Chemical Substance Management System

-
- Reflect the manufacturing/importing volume of chemicals registered in ERP to the chemical system and confirm their usage

-
- Manage the entire quantity of chemicals manufactured/imported through the chemical management system
- Select chemicals subject to registration based on annual volumes and fulfill government registrations within legal timeline
-
- Recognize unregistered chemicals
- Promptly report changes to registered chemicals to increase their the Companyight range
Pursuant to the Act on Registration and Evaluation of Chemicals, anyone who intent to manufacture or import at least 100 kg of a non-phase-in substance per year or at least 1 ton of a phase-in substance per year is required to submit analysis and evaluation data on the hazards and risks of the chemicals to the government and register them. Failure to register within the statutory timeframe* will result in the suspension and recall of the manufacturing, import, use, and sale of the chemicals, and violations could be punished by imprisonment with labor for up to five years or a fine not exceeding KRW 100 million.
To strengthen compliance with laws and regulations governing the manufacturing, import, and sale of chemicals, S-OIL has proactively implemented a chemical management system, which enables a systematic management of annual chemical manufacturing/import volumes, thereby allowing us to quickly select chemicals for registration and proceed with government registration within the statutory timeframe. The system reduces the risk of unregistered chemicals and is designed to allow for quick review and change reporting with automatic notifications when the weight range is increased upon registration. The system also dramatically reduces the workload by allowing chemicals registered in the system to be checked, rather than having to manually check each department.
non-phase-in substance and phase-in substance without a registration grace period: prior to manufacturing/importation
Phase-in substance: end of 2021 to end of 2030, depending on registration volume
Metrics & Targets
S-OIL proactively manages targets and achievements, including those related to air pollutants and hazardous chemicals, as part of its effort to comply with various environmental laws and regulations.
Metrics & Targets : Category, 2023 Targets, Performance in 2023, 2024 Targets, Mid/Long-term Targets
| Category |
2023 Targets |
Performance in 2023 |
2024 Targets |
Mid/Long-term Targets |
Total air pollutant emissions
(unit: ton) |
6,687
(including carry-over from 2023) |
4,440 |
Below 6,454 |
Below annual quota
of 2020-2024 |
Managing fugitive emissions
(unit: %) |
Below 0.08% |
0.03% |
Below 0.07% |
Maintaining below 0.07%
by 2025 |
| Enhancement of emergency response ability to leakage |
At least 2 emergency drills |
Conducted 2 emergency drills |
At least 2 emergency drills |
- |
| Zero oil spills |
Zero oil spills |
Zero oil spills |
- |
Registration of
chemical substances
with the government |
Completing chemical selection
for registration* and relevant
system implementation |
Completing chemical selection
for registration and relevant
system implementation |
Completing registration of all chemicals in scope |
Completing registration of all chemicals in scope by 2030 |
| Compliance with environmental regulations (penalties over USD10K) |
Zero violation |
Zero violation |
Zero violation |
Zero violation |
Manufactured/imported substances of 100-1,000 tons per year
New Businesses and R&D
Governance
Investment Decision-Making Structure
S-OIL has established a strategic investment process to ensure transparent and rational investment decision-making and to enhance the effectiveness of investments by systematically defining and implementing investment strategies consistent with corporate strategy. New investment projects proposed by the respective teams are subject to review and deliberation by an independent review team and the Management Committee (MC) before being submitted to the Board of Directors (BOD) for approval. For ongoing investment projects, a steering committee is formed for each project to oversee its implementation, management and operation, while a post-investment review process is established for completed projects. The Shaheen Project, the largest petrochemical project in Korea, received the final investment decision (FID) from the Board of Directors in November 2022, in accordance with the strategic investment decision process, and a steering committee has been established to oversee the progress of the project.
R&D Organizations and Processes

- Polymer Research
- Chemical TS&D Planning Team
- Polymer TS&D Team
- Polymerization / Catalyst Team
- Lube Research
- Lube R&D Team
With the completion of the TS&D Center in Magok Industrial Complex in October 2017, S-OIL made a successful entry into the petrochemical downstream business, and is focusing on strengthening R&D capabilities related to the existing lube business. Given the broad product spectrum in the petrochemical downstream sector, it is essential to develop new products that reflect customer requirements, provide necessary technical information, collaborate on processing technologies, and support analytical services. With this in mind, the TS&D Center focuses on securing technological capabilities and strengthening competitiveness in the petrochemical business by conducting R&D activities related to synthetic polymer resins produced at the Olefin Downstream Complex (ODC). It also multiplies chemical R&D capabilities by collaborating with academic institutions with the highest research capabilities in Korea. The Company also seeks to attract outstanding research talents in Korea to research renewable energy technologies in line with the global green/decarbonization trend.
S-OIL facilitates effective product development by considering customer needs and market changes, legal and regulatory requirements, and changes in business strategies when selecting product development tasks, and by encouraging the free exchange of ideas among members. The Company regularly reviews and provides feedback on the use of resources and research progress during the product development phase to ensure that research projects are carried out efficiently and successfully.
Strategy
Shaheen Project
S-OIL made the final investment decision for the Shaheen Project, a Phase II petrochemical expansion project, following approval by the Board of Directors in November 2022. The total investment for the project is USD 9,258 trillion, with mechanical completion expected in June 2026. Through the Shaheen project, the Company expects S-OIL to gain an additional 3.15 million tons of petrochemical production capacity, including approximately 1.8 million tons of ethylene per year, and steadily transform our corporate structure from a fuel-centric business portfolio to a fuel/petrochemical company. In particular, the project will more than double the annual ethylene production capacity in the Ulsan area, and the Company will be able to supply the product via pipeline to nearby olefin downstream facilities, reducing transportation costs and dramatically increasing the security of supply of domestic petrochemical feedstocks. The project also marks the world's first commercialization of Saudi Aramco's Thermal Crude to Chemicals (TC2C™) technology, which converts crude oil into petrochemical process feedstocks. The innovative new process is expected to improve energy efficiency and operational effectiveness, resulting in higher cost competitiveness and contributing to carbon emission reduction. Supported by the active cooperation of various stakeholders, including the governments of Korea and Saudi Arabia, major shareholders, and local communities, S-OIL will fully utilize its capabilities, including its successful experience in large-scale projects, outstanding competence, and the passion of its employees, to make the new investment a success. The R&D organization is also actively supporting the Shaheen project and is committed to expanding into the high value-added polymer business. When completed, the project will enable us to develop products that meet various customer needs, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), and provide technical support. Therefore, the Company will focus our R&D efforts on strengthening new technology capabilities in the olefin downstream segment in order to secure the necessary technological capabilities and enhance competitiveness.
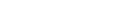
Timeline for Expansion of High Value Added Polymer Business
- 2024
- Introduce and validate PE polymerization/processing/analytical equipment
- 2025
- Introduce and validate PE polymerization/processing/analytical equipment, Actively reflect product development and technical support activities by identifying the needs of major customers
- 2026
- Strengthen marketing of high value-added polyethylene and technical support for customers
Diversifying Business Areas through Venture Investments
S-OIL actively pursues venture investments in companies in promising emerging technology fields as part of its efforts to secure future new technologies, seize new business opportunities, and contribute to ESG management. Our main venture investment targets are companies in fields that can strengthen our manufacturing competitiveness, create synergies with our existing businesses, have great potential to become new growth engines for the future, and contribute to ESG management. From 2019 to date, the Company has made direct investments in new energy, chemicals and materials, environment, mobility and smart plant. In 2023, the Company made new investments to enhance ESG management, one of which is EU CNC, a company that manufactures thermal insulation paints that are certified as green products for carbon reduction for heat shield and insulation, and S-OIL has made efforts to support the growth of the Company through PoC and CSR cooperation and to create business synergies with our business since the investment.
In light of recent changes in the business environment with the spread of the 4th Industrial Revolution, the strengthening of ESG management, and the transition to low-carbon and green energy, the Company plans to continue active investment and R&D in new energy fields such as clean ammonia/hydrogen, bio-based raw materials, and waste plastics.
Venture Investments Status
Venture Investments Status
| ~2020 |
- IPItechnology (polyimide)
- OnePredict (AI-based preventive machine diagnosis)
- LiBEST (Flexible battery)
- Glory & Tech (Overseas carbon emission reduction project)
- BEOMJUN E&C (sulfur polymer-based specialty construction materials)
|
| 2021 |
- KOHYGEN (hydrogen refueling station for commercial vehicles)
|
| 2022 |
- Allsu (waste oil collection platform)
|
| 2023 |
- EU CNC (thermal insulation eco-friendly paint)
|
Low Carbon Energy Business
To effectively respond to the energy transition, Fourth Industrial Revolution and circular economy trends, the Company is actively promoting new energy businesses such as low-carbon sustainable biofuels and circular products from biomass and plastic waste, as well as the introduction and use of low-carbon ammonia and hydrogen.
Biofuel / Circular Economy Business
Since 2024, the Company has produced low-carbon, environmentally friendly biofuels and circular products by co-processing crude oil with biomass and pyrolyzed waste oil, using its existing oil refining facilities to actively enter the market and create a value chain. In the first half of 2024, the Company began supplying the market with sustainable aviation fuel, renewable diesel fuel, and voluntary carbon reduction bio/circular products produced according to internationally recognized methodologies and certified by the International Sustainability & Carbon Certification (ISCC). The Company also plans to build a dedicated biofuel production facility to meet the ever-increasing demand for low-carbon and environmentally friendly products.
Hydrogen Business
In 2023, the Company signed a letter of intent (LOI) with our majority shareholder, Saudi Aramco, to introduce low-carbon ammonia, and as a follow-up, the Company is currently conducting various studies to secure the relevant infrastructure for the introduction, storage and transportation of low-carbon ammonia. To further our decarbonization endeavors, the Company is continuously exploring ways to use low-carbon hydrogen from the cracking of low-carbon ammonia as a feedstock and energy source, as well as ways to replace existing gray hydrogen, with the goal of achieving tangible results in the decarbonization field within the next five to six years.
Conducting Green & Decarbonization Research
Expansion Completion of S-OIL TS&D Center
S-OIL is strategizing R&D for sustainable growth in response to global environmental changes. To lead in the latest technologies and innovations, the S-OIL Technical Service & Development (TS&D) Center, which was completed in November 2023, was built with a total investment of KRW 144.4 billion (KRW 38.3 billion in Phase 1 and KRW 106.1 billion in Phase 2). Constructed on a gross building area of 36,700 m2 with four above-ground floors and two underground floors, the S-OIL TS&D Center serves as a hub of creative technological competitiveness. Equipped with the highest level of laboratory safety systems in Korea, it has a variety of support facilities, including state-of-the-art research laboratories, office and rest areas, a large auditorium, and an exhibition hall. Together with the Polymer Research Building and the Lubricant Research Building, which were completed in 2017, the center will play a pivotal role in the development of high-quality and high-value-added petrochemical and lubricant products, as well as lay the foundation for technology development in new energy fields such as clean hydrogen, ammonia and biofuels, in line with decarbonization and energy transition trends, reinventing S-OIL as a more sustainable and innovative company.
Strengthening Petrochemical Technology Capabilities
S-OIL is working to attract the Research & Development Center (R&D Center) of its parent company Saudi Aramco to the TS&D Center for research synergy in the field of green energy and decarbonization and is striving to cultivate domestic petrochemical technology capabilities and develop products and technologies through regular technology exchange meetings with SABIC, a subsidiary of Saudi Aramco and a global petrochemical company. In addition, the Company plans to conduct joint research with leading domestic and foreign research institutes to soft-land new research projects. While our R&D focus in the past has been on developing chemical technologies related to polypropylene and propylene oxide products and processes, the Company aims to broaden our petrochemical product range through the Shaheen project and expand research areas in line with the global trends of green energy and decarbonization.
Strengthening Lubricant R&D
Looking ahead, S-OIL aims to lead the development of innovative technologies in various fields, ranging from lubricants for existing internal combustion engines to lubricants for electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles, as well as developing fluid products that regulate the temperature of servers or electric car batteries. In 2023, the Company made significant progress in our efforts, including the development of 21 new lubricant products. The Company developed a long-life gasoline engine oil with a domestic patent in cooperation with Hyundai Motor Research Institute, and are also developing an automatic transmission fluid through continuous joint research. In line with the rapidly changing market environment, the Company is focusing our capabilities on the development of lubricants for electric vehicles and other innovative technologies, such as cooling lubricant products for temperature control in data centers, electric vehicles and batteries for energy storage systems (ESS).
Metrics & Targets
Low Carbon Energy Business Performance and Plans
2023 was a year in which S-OIL laid the foundation for the expansion of its bio-feedstock and waste plastic pyrolysis oil co-processing and hydrogen businesses. Building on this, the Company is now working to commercialize eco-friendly products that align with the global trend toward a circular economy.
Low Carbon Energy Business Performance and Plans : Performance,
| Performance |
- Regulatory sandbox approval from the Korean government for co-processing of bio-based feedstock and waste plastic pyrolysis oil
- Approval for waste plastic pyrolysis oil co-processing (July '23)
- Approval for co-processing of biobased feedstock (Dec '23)
- LOI signed with Saudi Aramco to introduce low-carbon ammonia (Oct '23)
- Initial batch delivered for biomass and waste plastic pyrolysis oil co-processing (Jan '24)
- ISCC certification obtained (April '24)
- Feasibility study for a dedicated sustainable aviation fuel plant (Nov '24)
|
| Plans |
- Engineering works for construction of a dedicated sustainable aviation fuel plant (within '25)
- Discussions and subsequent agreement with Saudi Aramco to introduce low-carbon ammonia (2024)
|
Clean Tech Production Capacity Expansion
Clean Tech Production Capacity Expansion : Co-processing, Dedicated Plant, 2024 ~ 2030
| unit : MTA |
2024 |
2025 |
2026 |
2027 |
2028 |
2029 |
2030 |
Co-processing |
2,360 |
55,000 |
80,000 |
80,000 |
80,000 |
80,000 |
80,000 |
| Dedicated Plant |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
520,000 |
520,000 |
It is based on production capacity on a maximum basis, so the actual production rate can differ from the above value due to market conditions.
Research and Technology Development Performance and Goals
S-OIL conducts its own research and development activities to develop new products, improve product quality, and upgrade production facilities without resting on the technology it currently possesses. The Company also conducts various joint research activities with leading domestic and foreign universities and research institutes.
Research and Technology Development Performance and Goals : Category, 2023 Targets, Performance in 2023, 2024 Targets, Mid/Long-term Targets
| Category |
2023 Targets |
Performance in 2023 |
2024 Targets |
Mid/Long-term Targets |
| Developing new PP products and applications |
Developing 4
new PP products |
Developed 5
new PP products |
Developing new PP products and applications |
Developing new polymer products and applications |
Technology development and
IP acquisition through strengthening collaborative research with external institutions |
3 external
joint research projects
15 patent applications |
3 external
joint research projects
17 patent applications |
Enhancing technological competitiveness
to secure new growth engines |
Natural Capital Management
Governance
The Sustainability Management team works on strategic natural capital management policies, while the Environment team conducts legally required audits, including environmental impact assessment, and proactively minimizes its impact on natural capital. The General Affairs and Government & Public Affairs teams also contribute to the enhancement of biodiversity in the communities where the Company operates, organizing a variety of activities to extend the positive environmental impact.
Strategy
S-OIL takes proactive biodiversity management as one of its key environmental policies. The Company has adopted a Biodiversity Policy and a No-deforestation Policy that goes beyond the mere reduction of negative impacts on biodiversity and seeks to actively contribute to the recovery and promotion of biodiversity.
Biodiversity Policy
S-OIL recognizes the critical importance of preserving biodiversity and is committed to minimizing our impact on the environment and biodiversity. We aim to achieve Net Positive Impact (NPI) on biodiversity by 2050 and have developed the following commitments to guide our efforts:
-
Net Positive Impact by 2050
S-OIL is dedicated to achieving Net Positive Impact (NPI) on biodiversity by the year 2050. We will implement actions that go beyond mitigating negative impacts, actively contributing to the restoration and enhancement of biodiversity.
-
Priority Area Targets
S-OIL is committed to avoiding potential adverse impacts on sites containing globally or nationally important biodiversity. We will exercise precautionary measures and refrain from conducting operational activities in proximity to such areas to prevent any potential harm.
-
Value Chain Responsibility
S-OIL will hold ourselves and our value chain partners accountable for minimizing biodiversity impacts. The Company will actively engage with our partners, encouraging them to avoid operational activities near sites with significant biodiversity value.
-
Mitigation Hierarchy
S-OIL strictly follows a mitigation hierarchy to manage our biodiversity impact effectively:
- Avoidance
- We will prioritize avoiding impacts on nature and biodiversity whenever possible in our operations and projects.
- Reduction
- In cases where avoidance is not feasible, we will take all necessary measures to limit and reduce our impact on ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Restoration
- We are committed to restoring areas and ecosystems adversely impacted by our business operations, fostering their recovery and resilience
- Offset and Compensation
- As a last resort, if any residual, adverse impacts remain after full implementation of the mitigation hierarchy, we will explore offsetting and compensatory measures to balance the biodiversity loss.
-
Biodiversity Risk Assessment
S-OIL will conduct comprehensive biodiversity risk assessments for our projects. These assessments enable us to identify potential impacts on biodiversity and implement appropriate measures to prevent or mitigate such impacts.
-
Stakeholder Engagement
S-OIL actively engages with stakeholders to foster collaboration and collective action for biodiversity conservation. The Company believe that collaboration is essential to address biodiversity challenges effectively.
No-deforestation Policy
S-OIL will take the lead in preventing forest destruction to protect forests, which are part of the environment and the home of life, and will continue to promote policies to protect forests and the earth by reducing industrial waste and expanding investment in greenhouse gas emission reduction. S-OIL will not create a business site that destroys forests in the future, and try to restore the forests when the company withdraw from the existing business sites. S-OIL will establish procedures to check the risk of forest destruction in the supply chain such as suppliers, and will make efforts to manage supplier ESG management and prevent forest destruction through an eco-friendly management system. Through sustainable environmental policies, S-OIL intends to implement "Zero Net Deforestation" by 2050, a promise of compensation through reforestation.
Policy Compliance
- Within the workplace, S-OIL will reduce emissions and expand investment in reducing greenhouse gas emissions through industrial waste recycling.
- S-OIL will make efforts to create forests and green areas in cooperation with related organizations near the workplace.
- Through the inspection of forest destruction risk of subcontractors and the eco-friendly management system, S-OIL will make efforts to expand forest creation and greening activities to subcontractors.
- S-OIL prepares internal procedures to check the risk of forest destruction when reviewing the expansion of business establishments and the operation of new business establishments.
- S-OIL secures a budget for cooperation with related agencies and strengthens its internal capabilities.
- S-OIL will make efforts to establish an evaluation process and conduct improvement activities to prevent environmental risks such as forest destruction of suppliers.
Risk Management
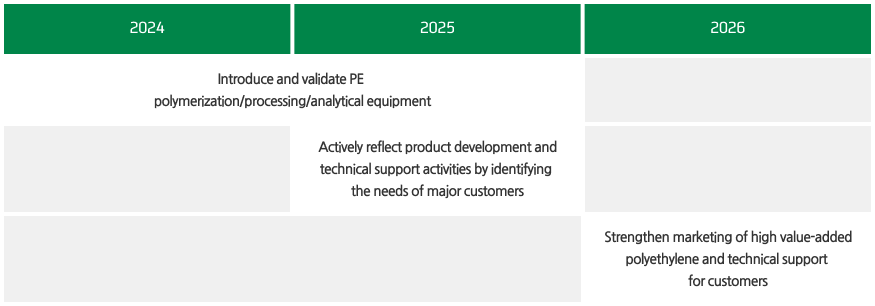
Utilizing the Biodiversity Risk Filter of the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF), the Company performed a risk assessment by accounting for both industry (oil, gas & consumable fuels) risks and regional (Onsan Refinery) risks. The assessment used dependency and impact as important assessment factors to recognize both the impact of natural capital on the economy and, conversely, the impact of corporate activities on society.
Concepts of Dependency and Impact
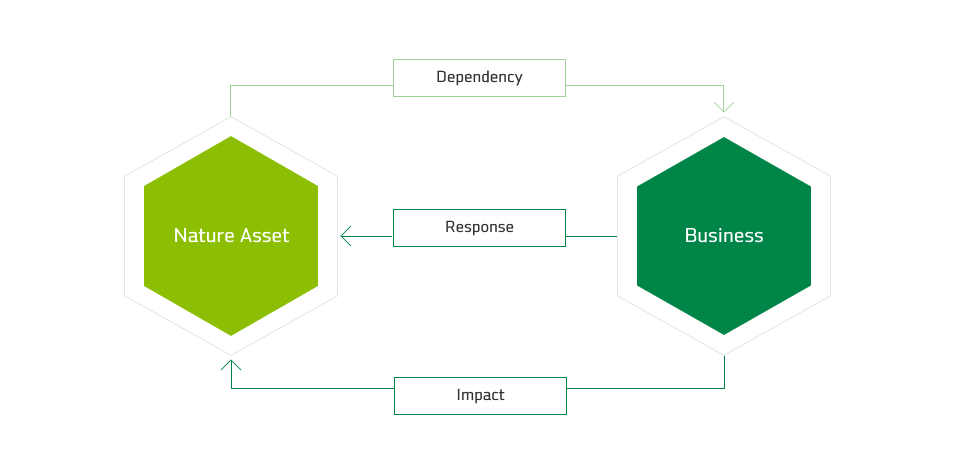 Nature Asset > Dependency > Business > Response/Impact
Nature Asset > Dependency > Business > Response/Impact
Risk Pool
Dependency / Impact : Type, Risk
| |
Type |
Risk |
|
Type |
Risk |
| Dependency |
Supply services |
Water shortages |
Impact |
Pressure on biodiversity |
Changes in use of land, freshwater, and oceans |
| Forest productivity and distance to markets |
Changes in forest cover |
| Limited wildlife availability |
Invasive species |
| Limited marine life availability |
Pollution |
| Regulating and supporting services (enabling) |
Land fertility |
Environmental factors |
Protected and conserved areas |
| Water quality |
Protected and conserved areas |
| Air quality |
Other critical areas |
| Ecosystem quality |
Ecosystem quality |
| Pollination |
Rarity |
| Regulating services (mitigating) |
Landslides |
Socioeconomic factors |
Indigenous people, community lands and territories |
| Wildfire risk |
Resource scarcity (food, water, air) |
| Plant/forest/aquatic diseases |
Labor and human rights |
| Herbicide resistance |
Economic inequality |
| Heat waves |
Additional reputational factors |
Media scrutiny |
| Tropical cyclones |
Political situation |
| Cultural services |
Travel attractiveness |
International regions of interest |
| Risk readiness |
Risk Assessment Process
- Identify industry- and location- specific risks

- Determine dependency/impact on the company

- Develop/implement/disclose response plan
Risk Identification
As a first step in identifying biodiversity risks in the area around the Head Office and the Onsan Refinery, the Company assessed the nature reserves around its sites. In addition, at some of our sites, the Company regularly conduct ex-post environmental impact assessments that include biodiversity. (Total 292 ha)
Key Biodiversity Areas Near Sites
Key Biodiversity Areas Near Sites : Business sites, Key Area, Classification, Distance
| Business sites |
Key Area |
Classification |
Distance (in straight line) |
| < 1km |
1 ~ 2km |
2 ~ 5km |
5 ~ 20km |
| Head Office |
Han River |
Key Biodiversity Areas |
|
● |
|
|
| Bamseom Island in Han River |
Ramsar wetland |
|
● |
|
|
| Onsan Refinery |
Evergreen Forest on Mokdo Island, Ulju |
Natural Monument (No. 65) |
● |
|
|
|
| Mujechineup, Ulju |
Ramsar wetland |
|
|
|
● |
| Taehwa River |
National Garden |
|
|
|
● |
Dependency and Impact Analysis
For the top five risk areas, the Company has taken action to minimize negative impacts on ecosystems near our operations and to help preserve biodiversity.
Risk Dependency and Impact Analysis
Risk Dependency and Impact Analysis : Risk, Dependency, Impact, Our response, Reporting page
Risk
(ecosystem services) |
Dependencies and impacts |
Our response |
Reporting page |
| Dependency |
Impact |
| Protected and conserved areas |
|
● |
- Environmental cleanup activities in the Mokdo Evergreen Forest
|
p. 87 |
| Pollution |
|
● |
- Air / water / soil / chemicals / waste management and legal compliance
|
p. 34-38 |
| Forest cover change |
|
● |
- Adopting a no deforestation policy
- EIA (ecosystem) and legal compliance
- Issuing e-receipts through mobile application
|
p. 37, 44, 51 |
| Tropical cyclones (regulating services) |
● |
|
- Maintaining natural disaster risk response manual
|
p. 28 |
| Labor and human rights |
|
● |
- Implementing a human rights policy and human rights audits
|
p. 74-76 |
Risk Response Efforts
Given the nature of our industry, the Company is keenly aware of the significant impact of onshore and offshore oil spills on the ecosystem, and the Company continually implement systematic measures to minimize negative impacts. At the same time, the Company adhere to stricter emission standards and regularly monitor air, water and hazardous chemicals. In addition, the Company is committed to making a positive contribution to the environment through ecological restoration activities in local communities.
Major Risk Response Activities
Major Risk Response Activities : Activity Type, Description
| Activity Type |
Description |
| Avoidance |
|
| Minimization |
- Reducing Emissions (Air/Water/Hazardous Chemicals, etc.) and Reusing Wate (p. 34-38)
- Onshore Leakage Management
- Establishing a rapid detection and first response system by installing 32 oil detectors and containment facilities in key areas of Refinery
- Additional oil detectors to be installed for more stringent monitoring
- Annual refinery emergency response exercises based on hazardous chemical and oil spill scenarios
- Marine Oil Spill Management
- Developing response scenarios for various possible marine pollution incidents
- Routine inspections of areas where liquid cargo transfer piping failures could lead directly to marine pollution due to dolphin-shaped pier structure
- Remote monitoring of the buoy, SPM's main facility located approximately 3 kilometers off the coast, with surveillance cameras.
- Enhancing surveillance capabilities with increased pixels on dockside CCTV in 2023
- Expanding investments in marine pollution prevention and response, including the construction of a large 150-ton pollution prevention vessel capable of more effective cleanup operations in offshore weather conditions.
|
| Restoration |
- Conservation efforts (such as saving endangered natural monuments, p.86-87)
|